Most Australian’s first connected with Amazon as the disruptive online book retailer sometime in the early 2000s. Amazon re-wrote the standards for print media retail, rendering bricks and mortar book shops obsolete with their formidable ecommerce supply chain. Success in books enabled Amazon to spread like wildfire, infiltrating every corner of the online market place. In February 2018, Amazon’s market capitalization surpassed Microsoft, leaving it ranked number three on the US Stock Exchange behind Apple and Alphabet, A.K.A Google (Balakrishnan 2018). In late 2017, Amazon entered the Australian marketplace and many Australian retailers are no doubt asking, what does this mean for me? Gerry Harvey, chairman of Harvey Norman was quoted as saying "Amazon is the worst possible corporate citizen to have in our midst. There's not a retailer in the world, practically, that likes Amazon" (Ming 2017).
Does Gerry have a point? Does Amazon’s entry into Australia really spell apocalypse for many Australian retailers? Or will Amazon’s entry invigorate Australian retail, providing a platform for new and existing businesses to work as strategic partners? Enabling the industry to ideate, innovate and further differentiate offers for it’s customers?
How does one respond when such a formidable organisation is added to an environment? Do you make a new friend? Partner with Amazon and look for common value. Do you fight? Go head to head with Amazon, providing an equivalent product or service and hope to keep your market share? Do you entrench? Back your differentiated model and bank on the fact that your offering can grow and thrive in the Amazon world? Or do you adapt? Look at how you can change what you are doing today and re-invigorate your competitive advantage? Whilst some might be taking the approach to just wait and see, many would advise that a more proactive approach is needed. As stated by Churchill (1948), “those who fail to learn from history are doomed to repeat it”.
This article will explore the history of Amazon and the strategies it has adopted to become the success it is today. It will reflect on strategies adopted by companies in the United States and assess how these strategies performed in a world with Amazon. It will identify similar Australian entities and strategies they can adopt to remain competitive. Finally, it will explore some of Amazon’s broader objectives and how their entry into Australia is likely to play a role in delivery of these objectives.
What do we know about Amazon?
Amazon have written a completely new play book on both “the long game” and “how retail can and should be executed”. These items complement each other perfectly and empower Amazon with a unique ability to create value for customers where others cannot. When Amazon say they are not focused on profits, it’s not just talk, they truly mean it. Amazon have a focus on growing market-share with little concern for profitability. Their core customer offering has three pillars:
1. Low prices
2. Prompt and Reliable Delivery
3. Vast Selection
(McGinn 2014; Magner 2017)
This genuine customer focus drives fast and sustainable growth in a manner that profit doesn’t have to be a key focus. Whilst many may think, not making profit is not viable, they should note there is a key difference between solvency and profit. Amazon’s cash flow is incredibly strong and because they keep expanding their market share, they continue to attract suppliers and investors to support and sustain their business model. The other important thing to note is Amazon are not sacrificing profit through negligence, they are opting to take these profits and re-invest in their business through activities like research and development. This re-investment ultimately drives greater opportunities to create new revenue and win market share from other competitors. When we look at Amazon’s history, they started as a book retailer and bit by bit moved into other products, then services and nowadays content and product generation. As Amazon has moved into each one of these markets it has had a ripple effect to varying degrees on all members within ecosystem. Figure 1 below illustrates an overview of Amazon’s history:
figure 1 – History of Amazon – (Sherman 2015; Hall 2018; Nasdaq 2018)
Challenges with Amazon
One thing to keep in mind is Amazon don’t necessarily use the same rule book that you do. When determining your strategic response, it will pay to be aware of some of the historic challenges other companies have experienced:
Amazon can always find a way to sell something cheaper – Stephen Herbert from X Fire Paint ball explained a situation where his business was selling on Amazon and he experienced something he described as “Amazon did an end run around us” (When Platforms Attack 2015). After a while Amazon went to X Fires suppliers and started selling the same products on Amazon, at a lower price than X Fire. What is more concerning is that Amazon’s price was not only lower than X-Fire, it was also lower than the manufacturers minimum advertised price. This holds true to Amazon’s philosophy of putting market share before profit and demonstrates their willingness to play the long game and starve competitors of revenue.
Amazon are not ashamed to replicate your offering - A study by Feng Zhu and Qihong Liu of Harvard Business School, found that in a 10-month period 3% of products that were posted on Amazon had knock off products created by Amazon (When Platforms Attack 2015). The knock off products were not necessarily better or cheaper, but when a customer searched for products of this category, the Amazon knock off was always promoted ahead of the original items in the search results.
Not selling too Amazon, doesn’t guarantee your goods won’t be sold on Amazon - For the longest time, Nike was resisting selling their products on Amazon. However, the state of retail in America created some factors that took this decision out of Nike’s hands. Liquidation sales from a large volume of failing department stores created a channel for Nike’s goods to find their way onto Amazon. This enabled Amazon to re-sell Nike product without any arrangements with Nike themselves. The situation put pressure on Nike’s revenue and forced them to come to the table with Amazon and strike up a deal during 2017 (Stevens & Germano 2017).
When does it make sense to work with Amazon?
Negativity aside, there are plenty of reasons why partnering with Amazon can be advantageous. It simply depends on where your business sits within it’s maturity cycle and your business’ long-term goals. If you are looking to expand your customer base, selling on Amazon will provide you access to upwards of 180 million shoppers a month in a truly global marketplace. In addition to this, ecommerce is here to stay and if you are yet to establish your online platform, working with a partner like Amazon will not only be more effective, but also quicker and cheaper than going about it yourself (McDougall 2017; Breslin, 2018). For every horror story you hear about Amazon, there are likely one, five, ten or more success stories. To set the context correctly, Amazon should not be viewed as a bad corporate citizen, you simply need to understand your business model and whether Amazon is the right vehicle to help you expedite the achievement of your goals.
As Amazon’s reach is massive and we have over 30 retail sectors we could discuss, for the purpose of this article, we will merely focus on fashion and electronics. Using the decision tree below a selection of varying candidates were chosen from these industries to help paint a picture of what works and what doesn’t:
During 2018 Amazon’s market share in the American fashion and apparel industry is expected to hit 28 billion USD (Peterson 2017). An impressive feat considering that they only sold their first garment in 2002. Amazon’s time in fashion has seen department stores lose significant revenue, brands like Quiksilver closing their US stores (Quiksilver in Ch. 11 2015) and companies like American Apparel and Sports Authority file for bankruptcy (Diakantonis 2016). However, amongst all this chaos there have been retailers that have gone from strength to strength. We’ll now look at why companies like Lululemon and TJ Maxx have been able thrive whilst companies like J.C. Penny have struggled to compete.
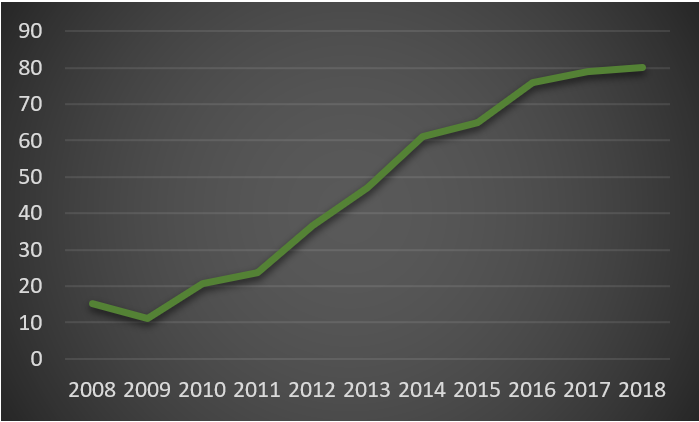
Lululemon have been able to differentiate themselves with a cult following for over 10 years now. This is a market segment where people buy a $119 pair of yoga pants to take their dog for a walk and pick up it’s business. Why you ask? Lulu have struck a chord with the health and fitness tribe. This is something that appeals to a vast amount of today’s marketplace, even those who aren’t so healthy or fit. Through high pricing and control of supply channels, Lulu have managed to keep their brand at a desired level of luxury and offer a unique customer experience when customers enter their stores. This tribe is not concerned with the low price, vast selection and fast delivery offered by Amazon. As a result, you won’t find them purchasing Amazon brand yoga pants for a quarter of the price. Lulu is our first example of how to execute the entrench strategy. Use a combination of brand affiliation and control over your supply channels and you will have a tried and tested approach to remain competitive against Amazon. Unfortunately, this level of brand loyalty is not something you build overnight, so in the event companies don’t have it today, they will likely struggle to build it in the next 12 to 24 months.
Lululemon Athletica Stock Price – (Nasdaq 2018)
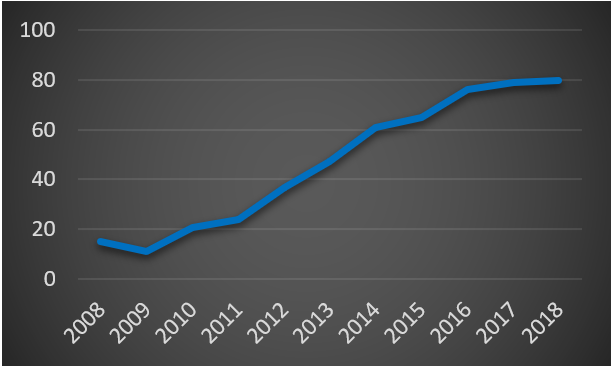
Next cab of the rank is TJ Maxx who hit’s a very different demographic to Lulu. TJ follow an off-price retail model which consists of selling high quality goods at very low prices. They commonly achieve this by selling garments that are off-season or on run out. The contraction of large entities like Sears has been a benefit to TJ Maxx as it has provided a pipeline of high quality goods being sold at discount prices (Gottfried 2017).
TJX Companies Stock Price – (Nasdaq 2018)
TJ Maxx appeal to a demographic that love the thrift shop experience and this is very difficult to replicate online. Whilst you can get cheap on Amazon, you can’t get the same “hunt the racks for buried treasure” experience that some shopaholics crave in a thrift shop. For that reason, TJ Maxx remains a strong competitor in the marketplace and is a great example of how you can differentiate your customer experience and entrench against a company like Amazon
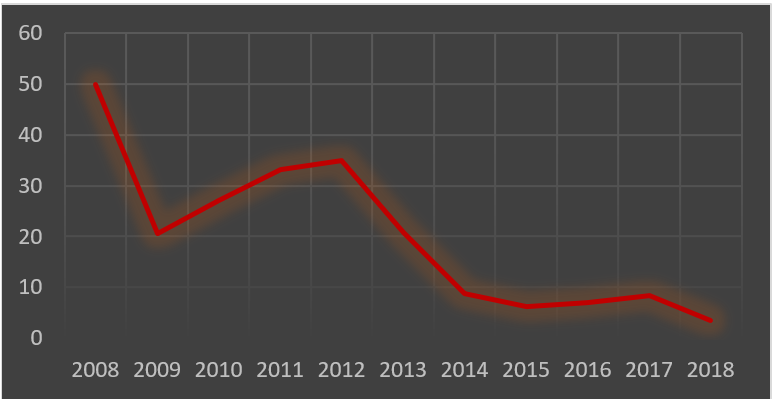
Kodak, Blackberry and the department stores all have something in common. They were big, they believed it would last forever and they were wrong. As noted by Thomas (2017) “Department stores have been tagged the laggards of retail today” and JC Penny is one of the many players in this position. Giving them the benefit of the doubt, we’ll say they had a strategy and it was to fight Amazon. It was to do exactly what Amazon was doing, but with a lower level of convenience and a less competitive price. What should also be concerning for these chains is that their constant closing of stores and liquidating of inventory plays into the hands of companies like Amazon on TJ Maxx. This gives these companies quality goods at low prices, enabling them to starve stores like JC Penny and Sears of further revenue.
J.C. Penny Stock Price – (Nasdaq 2018)
The facts are simple, market sentiment has shifted to a point where historic levels of bricks and mortar retail are not sustainable. Using this model and choosing to fight Amazon is a losing battle. Your best option is to adapt by slimming down your business and leveraging your existing capabilities coupled with new world technology to identify new revenue opportunities. Unfortunately, J.C. Penny and many other bricks and mortar fashion retailers in the United States are struggling to make this shift.
How can their Australian Counterparts Respond?
Lorna Jane (LJ), ironically another active wear company, can adopt very similar strategy to Lululemon and expect success. LJ has strong brand affiliation and manages this status by controlling it’s physical or digital retail channels. The organization is in the process of expanding it’s global footprint with stores in North America and Europe. LJ also works hard to differentiate itself by releasing “70-100 new products every month” (Fitzsimmons, 2015). As long as LJ can keep their niche market happy, the entrench strategy will be effective in the world of Amazon. A similar company that may have to assess it’s strategy is Michelle Bridge’s One Active. One Active is at a lower price point and likely doesn’t have the same level of customer brand affiliation as a LJ. Additionally, this brand is stocked at low cost shops like Big W, which limit’s One Actives control over it’s retail channels. Fighting or entrenching strategies will not work for One Active. They will need to explore either adapting their offering or partnering with Amazon as a retail channel.
When it comes to low cost fashion and apparel, Australia has a hoard of stores that will be in Amazon’s market share crosshair. Whilst fast fashion outlets like H&M and Uniqlo will weather the storm, stores like Big W, K-Mart and Target all offer a very similar and commoditised value proposition. Remove the decor and you’d be forgiven for not being able to differentiate each of the three retailers. As more Australian’s make the shift from physical to online shopping, these three chains will feel the pinch. They need to adopt an adaption strategy and they need to do it fast. An option for at least one of them could be moving into off-price retail…
The thrift market hasn’t reached it’s potential in the Australia, at least not the way TJ Maxx has managed to thrive in North America. This is likely this is why TJ Maxx has recently entered Australian shores looking to establish a bulk head with 35 Trade Secret outlets (Harris 2017). The closest other example of off-price retailers is the privately owned Direct Factory Outlets (DFO) which has a limited physical presence and no online capability. Big W, or one of the other offenders, have a great opportunity to get ahead of the game. They could start scaling back on their standard operations and converting them in to TJ Maxx style discount stores, targeting areas where DFO doesn’t have a presence. The wave of fashion and apparel liquidation is coming, so the first mover in this space could have a unique opportunity to convert some of their existing outposts in to discount resellers of off-price merchandise. This would enable them to not only maintain market share, but likely grow market share with new customer segments.
Moving into higher end fashion and apparel, our next stop is Myer. We have all been watching the demise of this Australian stalwart and unfortunately Myer still aren’t moving quickly enough to transform their 20th century retail model into something viable. Continuing in this manner will see them follow the same trajectory as Sears and J.C. Penny. As a first port of call, Myer need to scale back their retail floor space and focus solely on products that are exclusive and in demand. Myer can then use the newly vacated retail space to create new revenue streams. An option for this may be partnering with Amazon, offering them knowledge of the Australian landscape and a large bricks and mortar presence. Amazon could start utilizing Myer’s bricks and mortar space to pilot non-competing businesses like Amazon Go or Amazon Prime pickup points. A partnership with Amazon might also offer Myer valuable insights that can be applied to improve their core offering. In the event partnering with Amazon isn’t for Myer, they could look to adapt the left-over floor space, turning it into gyms, child care centres or other non-competing businesses. Whether they partner or adapt Myer need to find a solution that will generate new revenue from their existing assets, whilst not competing with their core offering. As a bonus, additional foot traffic generated by any new businesses will likely generate traffic for the heritage business.
Best Buy is our poster child when it comes to competing with Amazon in the electronics space. They have taken on somewhat of a hybrid strategy that has evolved over time. Initially Best Buy tried to fight Amazon on the price and delivery front. Whilst this had some success, they really made traction when they differentiated their customer service offering and did things that cannot be replicated by a machine (Roose 2017). Looking at Best Buy’s stock price, we see a direct correlation between their performance turnaround and when a series of newly implemented initiatives began making impact. New CEO Hubert Joly, who took over in 2012 and was the catalyst behind a number of these changes. So what can others learn from Best Buy?
Firstly, it’s better to lose money on a sale than give a customer to a competitor. If a customer was in a Best Buy store and asked them to price match Amazon, Best Buy did it. They applied the logic that the customer is here and may buy additional items, either now or in future and that purchase will offset this loss (Roose 2017). Best Buy are also doing their ecommerce well and have a strong online presence, which continues to grow in Amazon’s market place (La Monica 2017).
Best Buy Stock Price – (Nasdaq 2018)
Next, Best Buy have made a genuine investment in the happiness and well being of their staff. Some examples include perks like great discounts on stocked items. As well as keeping staff focused on the customer and not where their next paycheck is coming from by effectively managing restructuring activities. Finally, Best Buy have differentiated themselves by adding services like pre and post sales consulting on electronics purchases. This is something that Amazon see so much value in, they are trying to replicate it (Roose 2017). To summarise the Best Buy approach, they begun by fighting, then adapted parts of their business and service offerings and have now entrenched themselves in the electronics marketplace.
It’s no secret that Amazon creates a constant headache for Office Depot, in 2017 CFO Stephen Hare admitted “Amazon was stealing Business Solutions market share” (Kevin Moffitt - chief digital officer, office depot, inc 2017). Whilst Office Depot may not offer the answer for dealing with Amazon, they can offer some insight into what hasn’t worked. At this stage, Amazon may only have 10% of Office Depot’s market share, (Fitzgerald 2016) but what should concern Office Depot is that their revenue and profit have been effectively flat between 2012 and 2016. This implies that they are not growing and not lowering their operating costs.
Office Depot Stock Price – (Nasdaq 2018)
Adding to these concerns, their past cash cows of printer cartridges, paper and office basics are on the decline in an increasingly digital environment (FitzGerald 2016). It’s a given that Amazon will be able to provide Office Depots current offerings at lower cost and fast delivery, so the writing is on the wall that the flat revenue trend, will likely become a declining revenue trend. One other tactic that Office Depot tried was a failed merger with Staples. Unfortunately for both companies, US regulators blocked this merger in 2016 and Office Depots stock price has continued to fall since (McLaughlin & Harris 2016). Office Depot have applied a fight strategy which is not working for them, they need to adapt or revenues and margins will continue to drop.
How can their Australian Counterparts Respond?
JB Hi Fi (JB), a long-time performer of the Australian Electronics industry, will need to continue it’s Transformational Journey if it is to keep up with Amazon. Adaption is not new to JB who started out as a hi fi retailer and expanded into CDs, then consumer electronics, video games and white goods (JB H-Fi Limited Premium Report 2017). JB can learn a lot from the success of Best Buy and look to differentiate themselves on not only price, but also service offerings. JB should provision for a price war, doing what it takes to retain customers and market share. This will occasionally mean selling below cost, but as we observed sometimes you need to prioritise market share over profit. They also need to invest in their staff and ensure they offer the best customer experience possible. Some additional things that JB could bring to the market include partnering with local IT service providers to offer solutions like the Best Buy Geek Squad. We already see Airtasker making a play for this space, splashing their entertaining commercials on TV and simply replicating components of the Geek Squad offering. JB should be expanding into this market and offering a full end to end service for technology. Personal touches like this will also give JB a much higher probability of repeat business.
When you physically visit a Staples, Office Depot or Officeworks, you shouldn’t be embarrassed for asking someone which store you are in. Given the similarities in the three retailers and the negative impact Amazon has had on both Staples and Office Depot, it’s a fair assumption that Officeworks will suffer a similar fate. Even their strategy “Officeworks aims to provide customer with the widest range of products and great service at the lowest prices” (Wesfarmers Annual Report 2017) reeks of everything Amazon has spent the past 20 years perfecting. Adopting a fight strategy and attempting to beat Amazon at their own game with the products sold by Officeworks is not viable. Officeworks key customers a small and microbusiness (Hatch 2018) and if they are unable to differentiate their service in some way, they will continue to lose market share to Amazon. One thing Officeworks can do is keep adapting it’s in store services to keep people coming through the doors. Offer bookable conference rooms, 3D Printing, High Volume Printing, rental of items like drones and other expensive high-tech tools. These are areas Amazon is unlikely to play in and more importantly, they keep people coming into Officeworks 165 locations.
What is next for Amazon and where does Australia fit in?
Understanding Amazon’s masterplan and where Australia fits in, will help Australian retailers choose an appropriate strategy. As referenced earlier, Amazon make a significant investment in research and development, so it’s no doubt that something big is on their horizon, but what? From a business perspective there are some obvious targets that would allow Amazon to expand both market share and control over their supply chain.
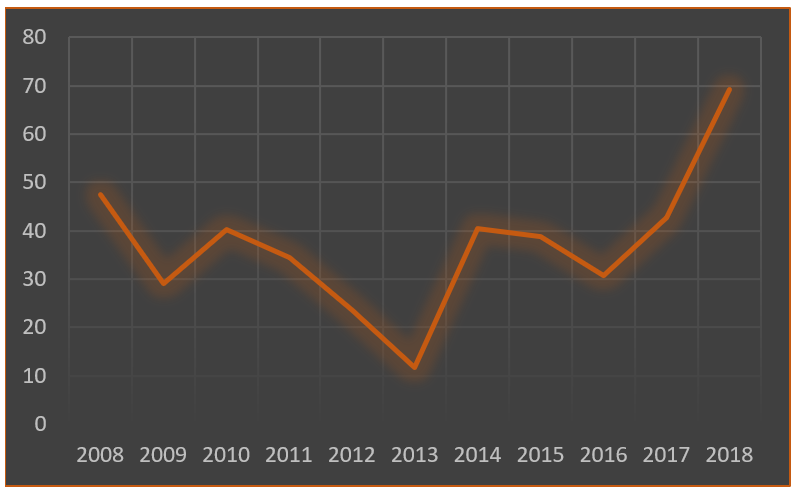
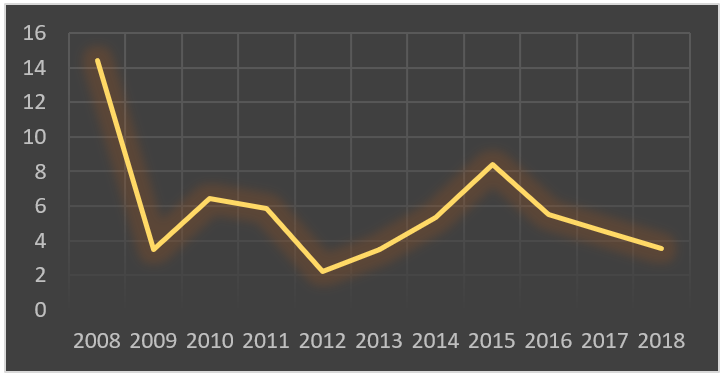
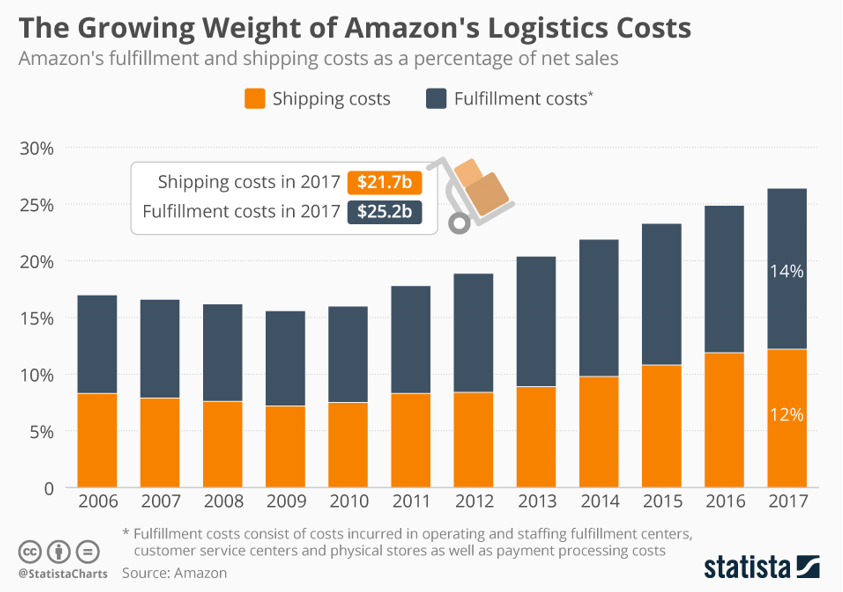
Global Logistics is a 2.1 trillion-dollar industry and key part of Amazon’s core offering. This is an area in which they are experiencing growing cost (figure 3 below) and still have external dependencies on companies like UPS and FedEx. Amazon has already dipped it’s toes into this area setting up spin off businesses like Shipping With Amazon (SWA) in America and a 240 strong van fleet in Munich. DHL reports that these Amazon vans have gobbled up one third of their market share in Munich (Haber 2017). In addition, Amazon are currently experimenting with shipping between China and North America (Camhi & Pandolph 2017) as well as contracting with airline Atlas Air for air freight (Berman 2018). It’s no coincidence Amazon selected Melbourne as it’s Australian hub as the port of Melbourne is the largest container port in Australia (Port of Melbourne 2018). This evidence builds a strong case that Amazon are making a move into logistics and Australia will likely be part of their test bed.
figure 3 –Amazon Logistics Costs – (Richter 2018)
After entering China as Joyo.com in 2004, Amazon has made little ground on the 80% market share currently held by Ali Baba (Haber 2017). China presents massive economic opportunity and if Amazon can secure a stronger presence, they will be poised to become the biggest kid on the block. Amazon’s move into Australia will strengthen their footprint in South East Asia and give them the ability to explore a few avenues to win over the Chinese Marketplace.
Finally, we should look at what is next for Amazon from a technology standpoint. Amazon are renowned as being industry leaders when it comes to technology driven business innovation. Some examples include how they reduced their warehouse operating costs by 20% as a direct result of Kiva Artificial Intelligence robots (Camhi & Pandolph 2017). Amazon also pioneered drone delivery in December 2016. A key challenge with all new technologies is the ongoing arm-wrestle with federal legislation and as a result Amazon have had challenges progressing some of their ideas. As an example, drone delivery has been significantly hampered by ongoing challenges with America’s Federal Aviation Administration (Morris 2015), meaning a place like Australia with less air traffic and potentially less regulation, could be a great test bed for Amazon’s drone technology. Moving on from drones, driverless vehicles have been in operation in Australian mines for some time. Australia may also prove a more accommodating landscape for Amazon to test driverless trucks and other vehicles.
Some Final Thoughts...
Amazon has been operating in America and other parts of the globe for just over 20 years. Some companies have gone out of business, some are struggling and others are continuing to thrive. The intent of this article has been to provide insight into not just Amazon, but what works and what doesn’t work. Here are a few closing sentiments:
Don’t enter a price war with Amazon - Amazon are happy to compromise profit to gain market share and market experts already indicate that Amazon will look to undercut Australian businesses by 30% (Magner 2017). In addition, don’t think that 30% discounts are a ceiling, when Amazon went into Whole Foods price cuts of up to 50% were seen across their stores (Valinsky 2018).
Be better, not bitter - Bagging Amazon and appealing to your customer base not to shop with them is simply providing free marketing for Amazon. Aussie Bob on the street will quickly forget that Amazon doesn't pay tax (Ming 2017) if he can get 100" TV from them at a 30% discount.
Don’t limit yourself to commodity products - Not only Amazon, but others in the market place can get a hold of your product and do exactly what you are doing. They simply need to do it for cheaper and longer than you can and you will be out of business.
Don’t put all your eggs in one basket – Whilst Amazon can offer you great opportunity, having them as your majority buyer could lead you to a situation where you lose control of your pricing. It’s simply good business practice to not have a single point of failure.
Ensure you have a point of differentiation - Offering equivalent products and services to Amazon will come down to a battle of attrition and Amazon will win. They are bigger, they are richer and they very good at what they do.
Look for the opportunity that will be created – Twain used the saying “during the gold rush it’s a good time to be in the pick and shovel business”. Review historic events, study the strategic indictors and use them to predict what future opportunities. We know that Amazon sales directly translates to things like a lot more packages being delivered, what other opportunities like this will be created for your business?
The world of retail existed before Amazon and the world of retail will exist after Amazon… Find your niche and keep your customers coming back. To quote Wylie (2018), “You’ll never beat Amazon at being Amazon, but Amazon can’t beat you at being you.”
References
Balakrishnan, A (2018) "Amazon surpasses Microsoft in market value for the first time", cnbc.com, 14-Feb-2018, 30-Mar-2018, https://www.cnbc.com/2018/02/14/amazon-surpasses-microsoft-in-market-value-for-the-first-time.html
Ming, C, (2017) "Amazon is the 'worst possible corporate citizen,' says Harvey Norman chairman", cnbc.com, 6-Mar-2017, 30-Mar-2018, https://www.cnbc.com/2017/03/05/amazon-is-the-worst-possible-corporate-citizen-harvey-norman-chairman.html
Churchill, W (1948)
McGinn, D, (2014) "The Numbers in Jeff Bezos's Head", Harvard Business Review, Boston Vol. 92, Iss. 11, (Nov 2014): 58-61
WHEN PLATFORMS ATTACK. (2015) Harvard Business Review; Boston Vol. 93, Iss. 10, (Oct 2015): 30-31.
Stevens, L & Germano, S (2017) "Nike Thought It Didn’t Need Amazon - Then the Ground Shifted", The Wall Street Journal Website, 28-Jun-2017, 30-Mar-2018, https://www.wsj.com/articles/how-nike-resisted-amazons-dominance-for-years-and-finally-capitulated-1498662435
McDougall, M (2017), "The Pros of Selling on Amazon and eBay", Shopify.Com, Blog, 10-Jan-2017, 30-Mar-2018, https://www.shopify.com.au/blog/6399562-the-pros-and-cons-of-selling-on-amazon-and-ebay
Breslin, S (2018), "Benefits of Selling on Amazon Instead of Your Own Store", Repricerexpress.Com, 30-Mar-2018, 30-Mar-2018, https://www.repricerexpress.com/benefits-selling-on-amazon-instead-store/
Peterson, H (2017) "Amazon just got one step closer to crushing America's biggest clothing stores", businessinsider.com.au, 21-Jun-2017, 30-Mar-2018, https://www.businessinsider.com.au/amazon-becomes-the-biggest-clothing-retailer-in-the-us-2017-6?r=US&IR=T
Quiksilver in Ch. 11 (2015) Value Retail News, November 2015, pp 10-11
Diakantonis, D. (2016) "Crunching Retail" Mergers and Acquisitions; Philadelphia Vol. 51, Iss. 12, (Dec 2016): 16-21.
Gottfried, M (2017) "New Retail Fashion: Consistency", Wall Street Journal , Eastern edition; New York, N.Y., 3-Apr-2017, pp B.11
Thomas, L, (2017) "JC Penney losses mount,missing estimates; stock craters", CNBC Website, 11-Aug-2017, 30-Mar-2018, https://www.cnbc.com/2017/08/11/jc-penney-q2-earnings-2017.html
Fitzsimmons, C, (2015), "Lorna Jane’s plan to double profits in three years", Australian Financial Review, 19-Mar-2015, 30-Mar-2018, http://www.afr.com/it-pro/lorna-janes-plan-to-double-profits-in-three-years-20150319-1m2z7z
Harris, C (2017) "Is NZ next for pioneering bargain store?", Sunday Star - Times, Wellington, New Zealand, 12-Mar-2017: D.5
Roose, K (2017) "Best Buy’s Secrets for Thriving in the Amazon Age", nytimes.com, 18-Sep-2017, 30-Mar-2018, https://www.nytimes.com/2017/09/18/business/best-buy-amazon.html
La Monica, P (2017) "Best Buy no longer eclipsed by Amazon", Money.CNN.Com, 23-Aug-2017, 30-Mar-2018, http://money.cnn.com/2017/08/23/investing/best-buy-stock-retail-amazon/index.html
Kevin Moffitt - chief digital officer, office depot, inc (2017), San Francisco: Boardroom Insiders Inc., 20-Nov-2017, Retrieved from https://search-proquest-com.ezproxy.lib.rmit.edu.au/docview/1979318460?accountid=13552
FitzGerald, D (2016) "Big Office Suppliers to Lay Out Strategies", Wall Street Journal (Online) ; New York, N.Y. [New York, N.Y], 16 May 2016, https://search.proquest.com/docview/1789100790?accountid=13552
McLaughlin, D & Harris, A (2016) "Staples-Office Depot Merger Collapses After Block by Judge", bloomberg.com, 11-May-2016, 30-Mar-2018, https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2016-05-10/staples-office-depot-merger-blocked-as-anticompetitive
JB H-Fi Limited Premium Report (2017), Ibisworld.com.au, IBISWorld Pty Ltd, June 2017, 13-Mar-2018
Airtasker (2016), “Jake gets his man cave hooked up - LIKE A BOSS”, YouTube, 14-Sep-2016, 30-Mar-2018, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GCKZOvEMD7I
Wesfarmers Annual Report (2017), wesfarmers.com.au, 19-Sep-2017, pp 40-43, http://www.wesfarmers.com.au/docs/default-source/reports/j000901-ar17_interactive_final.pdf?sfvrsn=4
Hatch, P. (2018). How officeworks plans to stay a 'category killer'. The Age, 8-Jan-2018, 30-Mar-2018, https://search-proquest-com.ezproxy.lib.rmit.edu.au/docview/1985295842?accountid=13552
Haber, J (2017), "Amazon’s Growing Transportation Network", Chain Store Age, Lebhar - Friedman Inc., January/February 2017, pp 20-21
Richter, F (2018) “The Growing Weight of Amazon's Logistics Costs”, statista.com, 13-Feb-2018, 30-Mar-2018, https://www.statista.com/chart/12893/amazon-fulfillment-and-shipping-costs/
Camhi, J & Pandolph, S (2017) "Amazon looks to further logistics automation", BusinessInsider.Com, 26-Apr-2017, 30-Mar-2018, http://www.businessinsider.com/amazon-looks-to-further-logistics-automation-2017-4/?r=AU&IR=T
Berman, J. (2018). "Amazon taking additional steps to expand its logistics portfolio" Logistics Management (2002); Framington Vol. 57, Iss. 3, (Mar 2018): 11-12.
Port of Melbourne (2018), portofmelbourne.com, 30-Mar-2018, http://www.portofmelbourne.com/about-us/quick-facts
Morris, C (2015) "Where can Amazon legally fly its drones?", Fortune.com, 20-Feb-2017, 30-Mar-2018, http://fortune.com/2015/02/18/amazon-drones-legal-countries/
FOR A.TV (2016), “A Day in the Life of a Kiva Robot”, YouTube, 11-May-2011, 30-Mar-2018, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6KRjuuEVEZs
Magner, L (2017) "Shoppers, get ready for Amazon", Money, Bauer Media Group, June 2017, pp16
Valinsky, J (2018) "5 ways Amazon has already changed Whole Foods", money.cnn.com, 9-Feb-2018, 30-Mar-2018, http://money.cnn.com/2018/02/09/news/companies/amazon-whole-foods-changes/index.html
Nasdaq (2018), nasdaq.com, 30-Mar-2018, https://www.nasdaq.com/
Wylie, M (2018) "Retail disruption: Adapt or die", NZ Business and Management, Adrenalin Publishing Limited, March 2018, pp 44
Sherman, E (2015) "20 years of Amazon's expansive evolution", cbsnews.com, 15-Jul-2015, 30-Mar-2018, https://www.cbsnews.com/news/20-years-of-amazons-expansive-evolution/
Hall, M (2018) "Amazon.Com", Britannica Online Encyclopedia, 9-Feb-2018, 30-Mar-2018, https://www.britannica.com/topic/Amazoncom